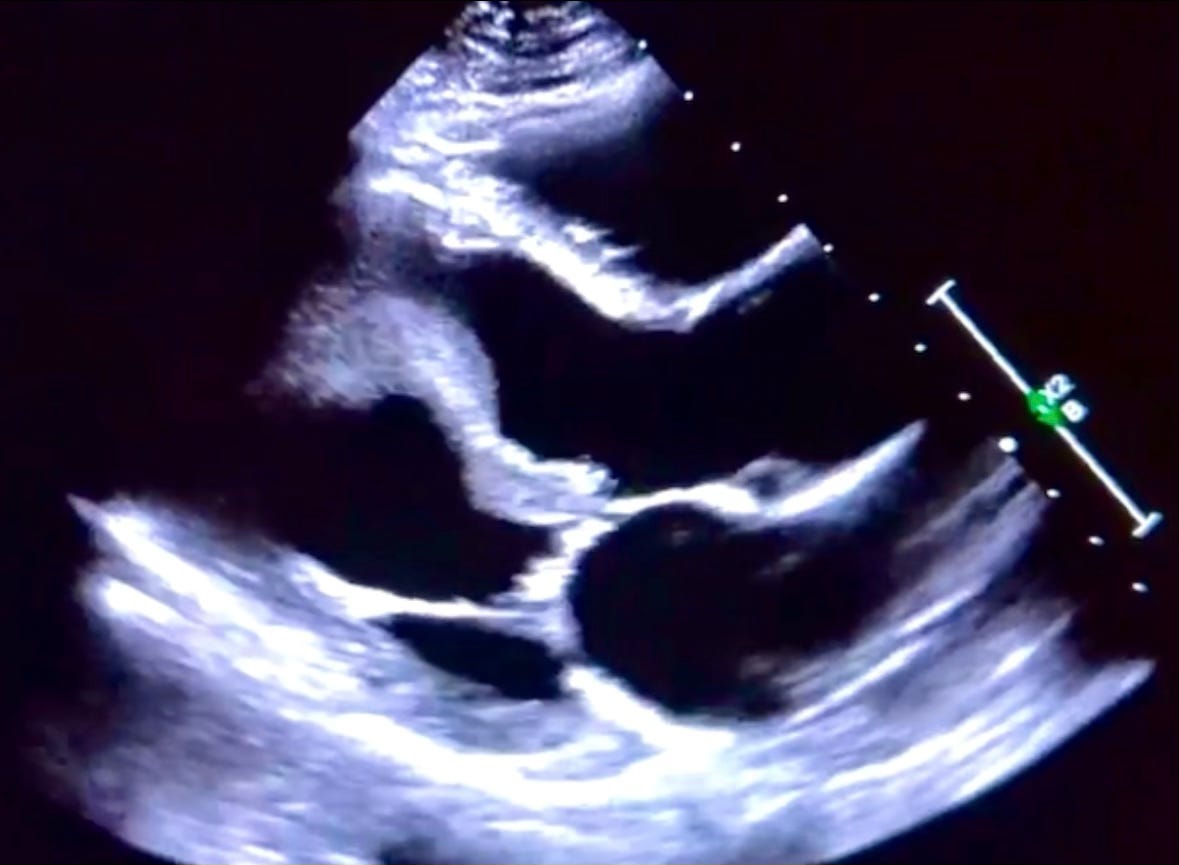
Large Snake-Like Thrombus
Something You Have Never Seen
Overview
A thrombosis is a gelatinous or solidified clot that can form within the blood vessels or inside of the heart. They tend to favor areas of stagnant flow or damaged endothelium.
These structures may obstruct circulation or embolize to other areas of the body such as the lungs (pulmonary embolism), brain (stroke), or lower extremities (artery or vein). Echocardiography is often utilized to rule out a cardiac source of emboli as the clinical team investigates its origin.
The formation of apical ventricular thrombi is commonly seen following acute myocardial infarctions as damaged tissue is exposed to the blood; fibrin, red blood cells, and platelets coagulate in the area of stagnant flow as a result. Multiple images below explore this large pedunculated thrombus and its mobile nature within the left ventricular outflow tract.